Many people overlook the importance of air filtration when considering indoor air quality (IAQ). A proper HVAC system should have a filter as part of the system. The air filters job in the HVAC system is to keep the units clean and help to avoid breakdowns caused by dirt and debris. Without a filter, the HVAC system may have problems draining water away as dirt gets trapped in the drain. There may be indoor coil issues that arise as unfiltered air blows across the wet coils and dirt and debris get stuck in the condensate and stick to the coil. The same problem applies to ductwork as the dirty air travels past the unit and into the ductwork. The dirty air catches in the ductwork and can cause improper airflow. In each case, water can be trapped and this in turn might allow mold and other allergens to grow and flourish. Even the most basic filter is better than no filter, not only your HVAC system but for your family in residential settings and employees in commercial settings. In 2018, Miami Valley residents used their heating and cooling systems a lot. In fact, according to Wunderground, we had 178 days with temperature highs below 60° and 108 days with temperature highs over 80° F. Meaning, most people used their HVAC systems over 75% of the year! That is a lot of time your filter is being used.
How it Works
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency describes indoor air pollution as one of the top five environmental health risks. For people with allergies, scientific studies have shown that air filtration reduces these airborne allergens and may provide some relief.
The World Health Organization has provided recommended standards covering three ranges of particle sizes, specifying guidelines for acceptable particulate matter concentrations. The human eye can only see particles as small as 25 to 60 microns – or the diameter of a human hair – but the particles that are most dangerous to human health are significantly smaller and invisible to the human eye (PM 2.5 and PM 1).
Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV) rating is determined by measuring particle counts upstream and downstream of the air-cleaning device being tested, the more particles removed by the filter, the higher the MERV rating. There are 12 particle sizes being tested. Dust spot efficiency is used to show how effective is at filtering smaller particle atmospheric dust from the air. Arrestance is the ability to filter to remove larger particles of dust. A High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filter can accomplish over 99.97% arrestance of these finer air particles.
CAUTION: As the MERV rating goes up it can affect the performance of your HVAC system. Adding a 15MERV filter to a system that was designed for 4 MERV increases resistance. The blower in the furnace or air handler is rated for a certain amount of pressure drop and increasing resistance increases the pressure drop which may cause reduced airflow throughout the system leading to reduced filtration, reduced comfort, the air conditioning coil to freeze up, and even the furnace heat exchanger to crack. Make sure your system is able to accept a higher MERV rated filter before installing. When considering replacing a HVAC system or just the filtration make sure a professional considers and verifies the system operation is correct.
Types
1-4 MERV
Setting for use: Standard Residential and Standard Light Commercial
Effectiveness: Use for up to 80% of larger particles and under 20% of smaller particles filtered
Examples of particles filtered effectively: Sanding dust, spray paint dust, and carpet fibers
Common filter types in this range: flat-panel fiberglass and washable/reusable
5-7 MERV
Setting For Use: Good Residential, Better Light Commercial, Industrial Workplaces
Effectiveness: Up to 90% of larger particles and up to 30% of smaller particles filtered.
Examples of particles filtered effectively: Pollen, pet dander, and hair spray
Common filter types in this range: 1-2” cotton pleated and flat-panel fiberglass
8-12 MERV
Setting for Use: Superior Residential, Good Light Commercial, Commercial, Good Industrial Workplaces
Effectiveness: Up to 95% of larger particles and up to 75% of smaller particles filtered
Examples of particles filtered effectively: Welding fumes, auto emissions, milled flour, lead dust, pollen, household dust, lint, mold spores, Legionella, and dust mites
Common filter types in this range: 1-2” cotton pleated, media panel filter, and extended surface deep pleated
13-16 MERV
Setting for Use: Hospitals and Health Care Facilities, Superior Residential, Superior Commercial, Superior Industrial Workplaces
Effectiveness: Greater than 95% of larger particles and greater than 98% of smaller particles filtered.
Examples of particles filtered effectively: Tobacco smoke, general smoke, all bacteria, Droplet Nuclei (sneeze), cooking oil, smog, virus carriers.
Common filter types in this range: Media panel filter, extended surface deep pleated
17-20 MERV
Setting for Use: Specific Commercial Applications; Cleanrooms, Radioactive Materials, Pharmaceuticals, Carcinogenetic Materials
Effectiveness: 100% of larger particles and 99.97% or greater of smaller particles filtered.
Examples of particles filtered effectively: All combustion smoke, carbon dust, viruses
Common filter types in this range: Fiberglass and nonwoven fabric material
View MERV Rating Chart
Comfort
When it comes to comfort and air filtration, a proper analysis by an advisor needs to be made. Many factors come into play such as: what type of building is it, does anyone have any allergies, does anyone have a weak immune system, and can the MERV be increased without compromising the airflow? Other factors that play a role in comfort are cost of installation and the cost of replacement filters.
Did you know?
- 50% of all illnesses are caused or aggravated by poor indoor air quality according to The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. A study cited by Kimberly-Clark Corporation found that for every 10 workers, poor indoor air quality caused an additional 6 sick days per year.
- The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) states poor indoor air quality can cost businesses up to $168 billion annually. Medical care and absenteeism contribute significantly to those costs.
- Employers can increase workforce performance by roughly 10 % by implementing indoor air quality solutions – DOE.
- By controlling contaminants such as dust mites, asthma cases can be reduced by 55 to 60% – The American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
DIY
Using an air filter is just one step toward improving the overall quality of indoor treated air. Here are some other things you can do to help IAQ:
- Do not smoke in the building
- Use a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter to reduce dust, dander, and other allergens
- Keep humidity in your home below 50% year round
- If you have a pet, groom the pet outside the home to reduce the amount of pet dander in the air.
- If you have tiled floors or walls, make sure to they are kept clean to reduce the potential for mold growth.
- Check and/or change your filter regularly, check at least once a month, if you have pets, once every two weeks.
- Use Zero and Low VOC paint indoors
- Spray paint in garage or outdoors
- Plants, natural air purifiers, but beware if you suffer from allergies, they may hurt more than help.
- Candles, limit use or use beeswax candles, which let off less smoke.
- Professional carpet cleaning, they can treat for pets and allergens in the carpet as well.
- Make sure to turn on the exhaust when you are cooking, this can greatly reduce oil and smoke.
Service
Make sure to check and/or change the filter regularly, with pets every two weeks, no pets, check once am month
At Hauck Bros., Inc., our Gold and Platinum Home Comfort Protection Plans come with Media Filter replacement included in the plan at the time of the maintenance inspection. Media Filter Replacement can also be added to the Silver plan for as low as $7 per month.
Accessories
Thermostat, Some models have maintenance features that will remind you to check/replace the filter
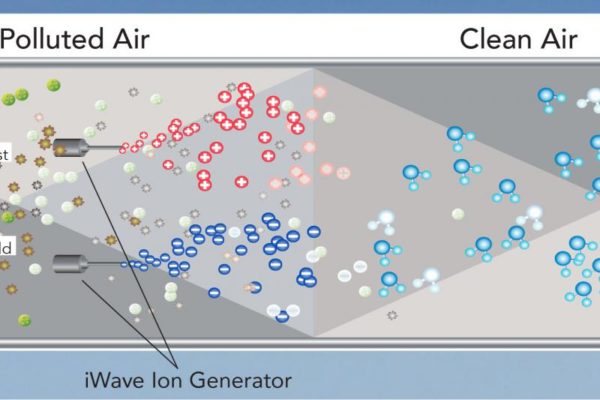
Ionizer, uses high voltage to ionize (electrically charge) air molecules. Negative ions, or anions, are particles with one or more extra electron, conferring a net negative charge to the particle. Effective against other particles normally reserved for a higher MERV count. Examples, viruses, bacteria, mod spores, and smoke.
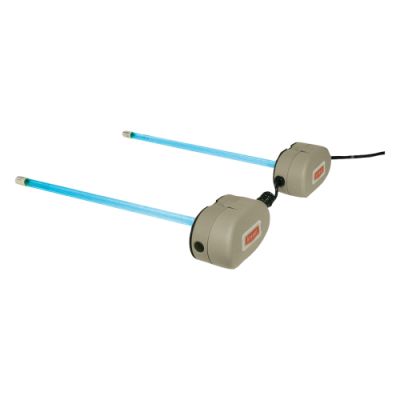
Ultraviolet (UV) Light, designed to help eliminate mold, bacteria, viruses, and other allergens that can be circulated in the air.